These costs may be higher because technology is often more expensive when it is new than it will be in the future, when it is easier and more cost effective to produce and also more accessible. The same will likely happen over time with the cost of creating and using driverless transportation. The CVP relationships of many organizations have become more complex recently because many labor-intensive jobs have been replaced by or supplemented with technology, changing both fixed and variable costs. For those organizations that are still labor-intensive, the labor costs tend to be variable costs, since at higher levels of activity there will be a demand for more labor usage. Assuming factors like demand and competition are equal, the company should make the product with the highest return relative to variable costs in order to maximize profits. Thus, the contribution margin ratio expresses the relationship between the change in your sales volume and profit.
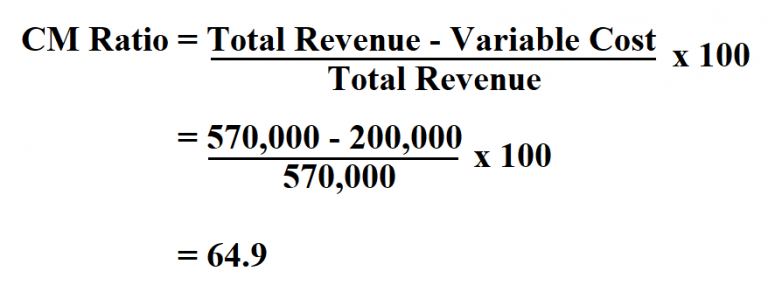
- The contribution margin is calculated by subtracting variable costs from revenue, then dividing the result by revenue, or (revenue – variable costs) / revenue.
- Regardless of how much it is used and how many units are sold, its cost remains the same.
- It is important to note that the contribution margin should not be considered in isolation.
- Contribution margin is used to plan the overall cost and selling price for your products.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
Variable expenses directly depend upon the quantity of products produced by your company. For example, if the cost of raw materials for your business suddenly becomes pricey, then your input price will vary, and this modified input price will count as a variable cost. While there are plenty of profitability metrics—ranging from the gross margin down to the net profit margin—the contribution margin metric stands out for the analysis of a specific product or service. In the United States, similar labor-saving processes have been developed, such as the ability to order groceries or fast food online and have it ready when the customer arrives. Do these labor-saving processes change the cost structure for the company?
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
It includes the rent for your building, property taxes, the cost of buying machinery and other assets, and insurance costs. Whether you sell millions of your products or 10s of your products, these expenses remain the same. The contribution margin is the amount of revenue in excess of variable costs. One way to express it is on a per-unit basis, such as standard price (SP) per unit less variable cost per unit. The formula to calculate the contribution margin is equal to revenue minus variable costs.
What Is the Difference Between Contribution Margin and Profit Margin?
In fact, we can create a specialized income statement called a contribution margin income statement to determine how changes in sales volume impact the bottom line. Contribution margin analysis also adding new users in xero helps companies measure their operating leverage. Companies that sell products or services that generate higher profits with lower fixed and variable costs have very good operating leverage.
Formula to Calculate Contribution Margin Ratio
It represents the incremental money generated for each product/unit sold after deducting the variable portion of the firm’s costs. But what is considered “good” largely can depend on your industry. This is because the contribution margin ratio lets you know the proportion of profit that your business generates at a given level of output. Direct Costs are the costs that can be directly identified or allocated to your products. For instance, direct material cost and direct labor cost are the costs that can be directly allocated with producing your goods. So, you should produce those goods that generate a high contribution margin.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
The gross margin shows how well a company generates revenue from direct costs such as direct labor and direct materials costs. Gross margin is calculated by deducting COGS from revenue, dividing the result by revenue, and multiplying by 100 to find a percentage. The contribution margin formula is calculated by subtracting total variable costs from net sales revenue. With a contribution margin of $200,000, the company is making enough money to cover its fixed costs of $160,000, with $40,000 left over in profit.
It also helps management understand which products and operations are profitable and which lines or departments need to be discontinued or closed. The contribution margin measures how efficiently a company can produce products and maintain low levels of variable costs. It is considered a managerial ratio because companies rarely report margins to the public. Instead, management uses this calculation to help improve internal procedures in the production process. Fixed costs are costs that are incurred independent of how much is sold or produced. Buying items such as machinery is a typical example of a fixed cost, specifically a one-time fixed cost.
We will discuss how to use the concepts of fixed and variable costs and their relationship to profit to determine the sales needed to break even or to reach a desired profit. You will also learn how to plan for changes in selling price or costs, whether a single product, multiple products, or services are involved. Using this metric, the company can interpret how one specific product or service affects the profit margin. The fixed cost like rent of the premises, salary, wages of laborers, etc will remain the same irrespective of changes in production.