The additional $10,000 was part of a major donor’s contribution that was temporarily restricted to complete the project, but the donor agreed to release it from restriction when the project was completed. So, the additional $10,000 could be added to the organization’s unrestricted funding and used for other initiatives. In cases like these, the non-profit would recognize the donation as permanently restricted contribution revenues on the statement of activities and it would increase permanently restricted net assets on the balance sheet. Restricted funds are any donations made and earmarked for a specific purpose by the donor. Donors have the legal right to restrict the donations they contribute to organizations (typically nonprofits) and require that their gifts be used only for very limited and specific purposes. This type of situation is possible when the $500,000 the organization has in the bank is restricted for a specific purpose.
What Is Restricted Cash on a Balance Sheet? With Examples
The newly released not-for-profit reporting standard retains the current approach, focusing on the organization as a whole and providing a uniform reporting format across varying industries in the nonprofit sector. A restricted fund contains money that is earmarked for use only for a specific stated purpose. If the money is temporarily restricted, any excess can become unrestricted once the purpose is fulfilled. If the money is permanently restricted, it must be kept intact in the form of an endowment, usually in perpetuity, and only the interest earned by investing the endowment may be spent in service of the purpose. Nonprofit employees should be trained to identify expenditures that require allocation to restricted funds.
Why Do Companies Give Out Restricted Stock?
Restricted stocks are nontransferable and must be traded according to the relevant Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations. The restrictions of these stocks usually relate to their vesting period, which is when they can’t be sold or transferred. This should make that method more appealing because it reduces the complexity in preparing the statement, as well as its overall length. Nonprofit organizations can avoid confusion about how they intend to spend a donor’s funds by offering a choice of designation. A cancer research nonprofit, for example, could give donors a choice to allocate their funds to any one of breast, skin, or brain cancer clinical trials.
What happens if restricted funds are spent for a non-designated purpose?
Other times, a donor will make a contribution earmarked for a specific purpose. Perhaps the donation is to be used on a specific project or to pay for a specific need the non-profit has. This could be for a specific construction project, the purchase of a vehicle, or for a specific program operating within the non-profit. A restricted asset is cash or another item of monetary value that is set aside to use for a particular stated purpose, primarily to satisfy regulatory or contractual requirements. Our fund accounting experts here at Jitasa specialize in helping nonprofits and other organizations in the social good sector keep their finances well-organized and maintained. However, it’s expensive, time-consuming, and reputation damaging if you misallocate and misuse your funds, even by mistake!
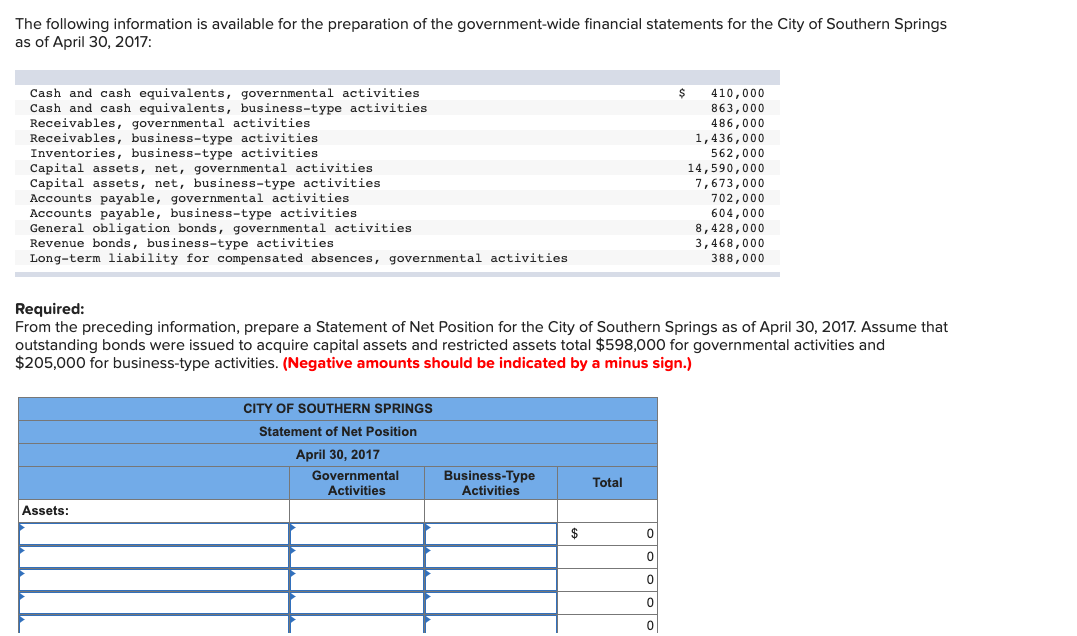
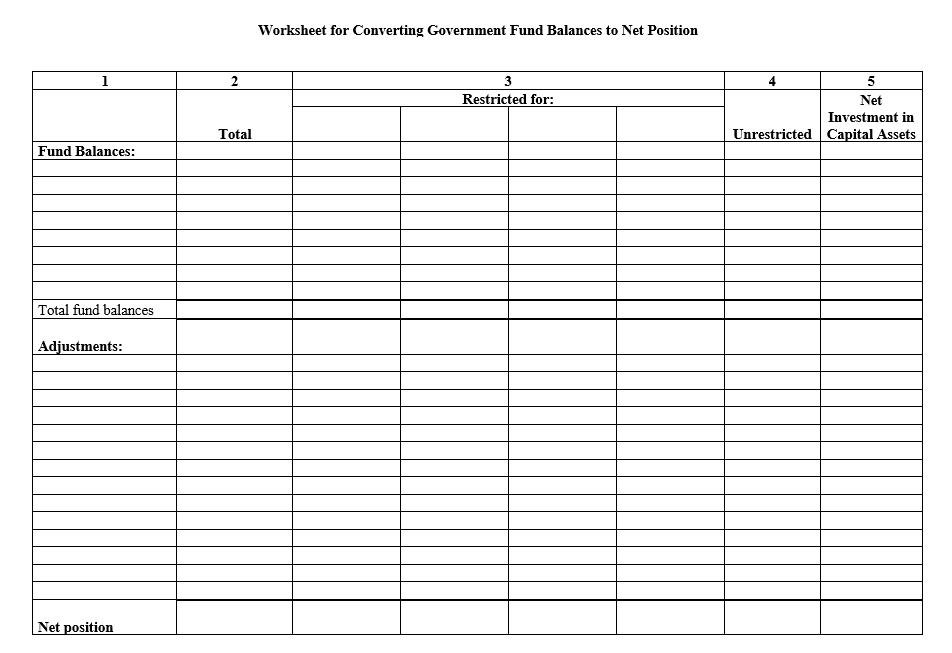
- The sum of these three classifications of net assets gives the total net assets for the non-profit.
- If a nonprofit fails to honor restrictions and these indiscretions are discovered via financial audit or annual tax forms, they may face major penalties from the IRS, including the potential loss of their exempt status.
- Instead, employees automatically receive shares when the restricted stock vests.
- Using the Andrew Carnegie example, if Carnegie stipulated that the dividends from his donation were to be used for a specific purpose, those dividends would be treated as a temporarily restricted assets as they are received.
8A Restricted assets – before adoption of ASU 2022-03
With employee stock options, the employee must pay the exercise price of the option to receive the shares. Typically, fund designation is specified in writing in what is termed the gift instrument. Foundations that provide restricted funds often describe how they want their money allocated when they distribute the award. A donor of restricted funds to a nonprofit usually designates what the money can be used for in a written document called the gift instrument.
Instead, the separation should be dealt with by accounting practices on the nonprofit’s financial statement. Once you have viewed this piece of content, to ensure you can access the content most relevant to you, please confirm your territory. One of the most critical is the difference between unrestricted net assets and restricted net assets. This doesn’t mean restricted funds are always a major challenge or hassle for your organization! For example, during a capital campaign, the nonprofit may self-restrict the donations coming from major contributors during the quiet phase of the campaign. These funds must be used to fund the program or project that the capital campaign is dedicated to.
The non-profit doesn’t have owners, for example, making shareholder equity an inapplicable label. Net assets is more descriptive, implying that the number represents the net difference between the non-profit’s assets and its liabilities. Click here to extend your session to continue reading our licensed content, if not, you will be automatically logged off. Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, what are restricted assets and richer. The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation. Whether you’re analyzing a non-profit’s financials before making a donation, as part of your job, or just out of curiosity, there are a few basic differences between the for-profit world and not-for-profit world that you must understand.
Another critical element is the Statement of Cash Flows, which details the cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. This statement helps stakeholders understand the liquidity and financial flexibility of the organization. This dual categorization provides insights into how efficiently the organization is using its resources to achieve its mission. Previous FASB standards required nonprofits to separately report investment expenses; they can now report investment returns net of investment-related expenses. This change should make it easier for not-for-profits to report investment activities and provide greater comparability among organizations using internal and external investment managers.